Communication fundamentals: Become a Effective managers and professionals
Business communication is the basis for the success of any organization regardless of its size, industry, or business model it operates in. Being able to communicate effectively, communication Style are the foundation of successful interactions, whether in personal relationships, professional settings, or broader societal contexts. Communication skills are the abilities and competencies to send and receive messages in all forms verbal, non-verbal, written and visual. These skills cover a multitude of skills to express yourself clearly, your thoughts, ideas and emotions and navigate through interactions with others and receive messages from others.
Fundamental of Communication Style
Communication is the process of exchanging information by speaking, writing, reading, Listening or use some others medium to interact with the people.
Effective business communication is how employees and management interact to reach organizational goals. Its purpose is to improve organizational practices and reduce errors

Objectives of communication Style
The objectives of communication are many and varied depending on the context and purpose of the communication. Here are some of them:
Share Information: One of the main objectives of communication is to share information. This includes sharing facts, data, instructions, updates, news and other relevant information to individuals or groups.
Create Understanding: Communication aims to create understanding among individuals or groups by exchanging ideas, opinions and perspectives. It means the message sent is received and interpreted correctly by the intended audience.
Build Relationships: Communication plays a big role in building and maintaining relationships. It creates connections, trust, rapport and mutual respect among individuals or groups through interactions, conversations and dialogue.
Influence Behavior: Another objective of communication is to influence the behavior, attitudes, beliefs or decisions of others. This may involve persuasion, motivation, encouragement or advocacy to achieve specific goals or outcomes.
Solve Problems: Communication helps in problem solving by enabling individuals or groups to identify issues, discuss solutions, collaborate on ideas and reach consensus. Effective communication helps in resolving conflicts, addressing challenges and making informed decisions.
Express Emotions: Communication allows individuals to express their emotions, feelings, needs and desires. It provides a platform for emotional expression, empathy, support and connection with others.
Give Feedback: Communication involves giving feedback to individuals or groups on their performance, behavior or actions. Feedback helps in assessing progress, identifying areas for improvement and reinforcing positive behaviors.
Achieve Goals: Communication contributes to the achievement of individual, organizational or societal goals by aligning efforts, coordinating activities and mobilizing resources. It ensures clarity of purpose, direction and expectations to achieve goals.
Promote Collaboration: Communication promotes collaboration and teamwork by sharing information, coordinating and cooperating among team members or stakeholders. It promotes synergy, creativity and innovation through collective efforts.
Personal Development: Communication supports personal development by promoting self-expression, self-awareness and interpersonal skills. It encourages active listening, empathy, adaptability and continuous learning for personal growth and improvement.
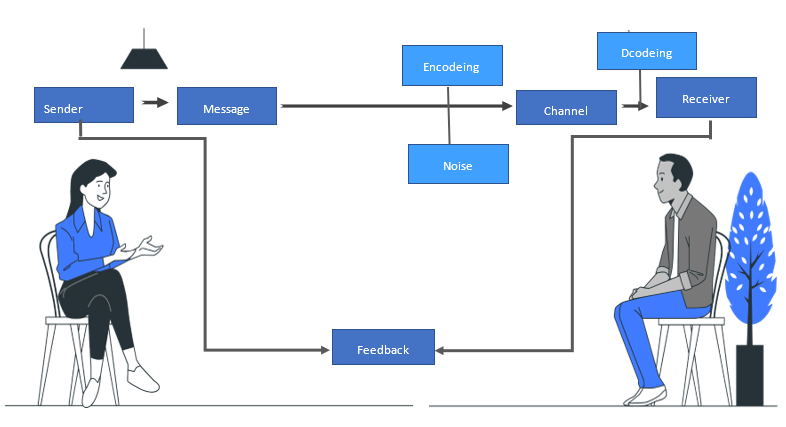
The elements of communication Style And communication cycle
- Sender
- Message
- Encoding
- Noise
- Channel
- Decoding
- Receiver
- Feedback
Types of Communication

Verbal communication is a type of communication skill where the information, emotions and thoughts are exchanged from one to others using any word, speech or spoken language.
Example: Public Speaking, Talking face to face in conversation.
Non-verbal communication is a type of communication skill where the information transfer one person to another person without using any word or spoken language.
Example : Body language, Touch, Eye-contact, etc.

Visual communication is a story-telling, it’s how we communicate information and create experiences across a range of visual mediums.
Example :Infographic, Image, Video.
Written communication is any written message that two or more people exchange. Written communication is typically more formal but less efficient than oral communication.
Example: Menu card, Shopping lists, Advertisements, etc.

Models of Communication
The communication will be held between two people. There is a sender who always send the message and a receiver who always receive the message. It is a one-way communication method.
Ex: Public Speaker, Brand Story
The communication is a two way communication method of exchanging various information or ideas. Here the sender can work as receiver and receiver can work as a sender.
Ex: WhatsApp, Facebook, Email
This communication occurs between two or more people for exchanging many information or message. In this communication both of the sender and receiver influence.
Ex: Video meeting, Cold Call
The 7 C’s of communication
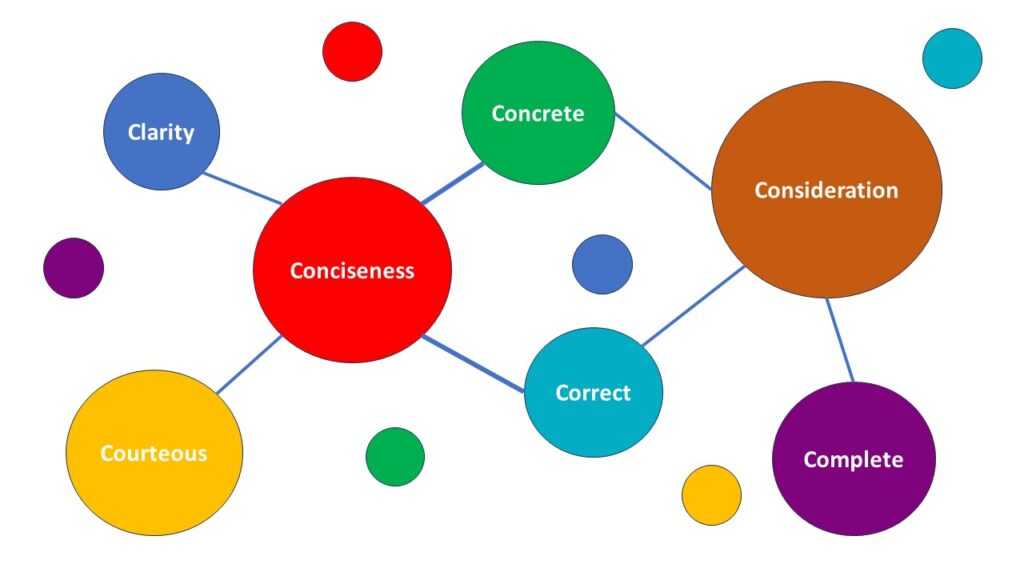
The 7 C’s of communication are a set of principles that are essential for effective communication:
Clarity: Ensure your message is clear and easy to understand. Avoid jargon, ambiguity and complexity.
Conciseness: Say what messages to your audience can understand with as few words as possible. This helps preserve their attention span and prevents misunderstanding.
Concreteness: Use language that describes specific things rather than general ideas or concepts; make the message visualizable.
Correctness: All messages should be correct in terms of grammar, punctuation, spelling and facts – mistruths destroy trust quicker than anything else.
Consideration: Think about who you are speaking to before crafting any content for dissemination ; understand their needs at this particular point in time then speak from there – it’s not about you but rather them always.
Completeness: Avoid leaving out any vital details from which questions might arise later by failing to provide all necessary information upfront thereby sowing seeds of doubt within minds coming across such incomplete records.
Courtesy: Always be polite while communicating regardless of platform ; never use offensive words when addressing others unless intentionally trying so perhaps only during comedy shows meant exclusively for adults.
Effective communication strategies
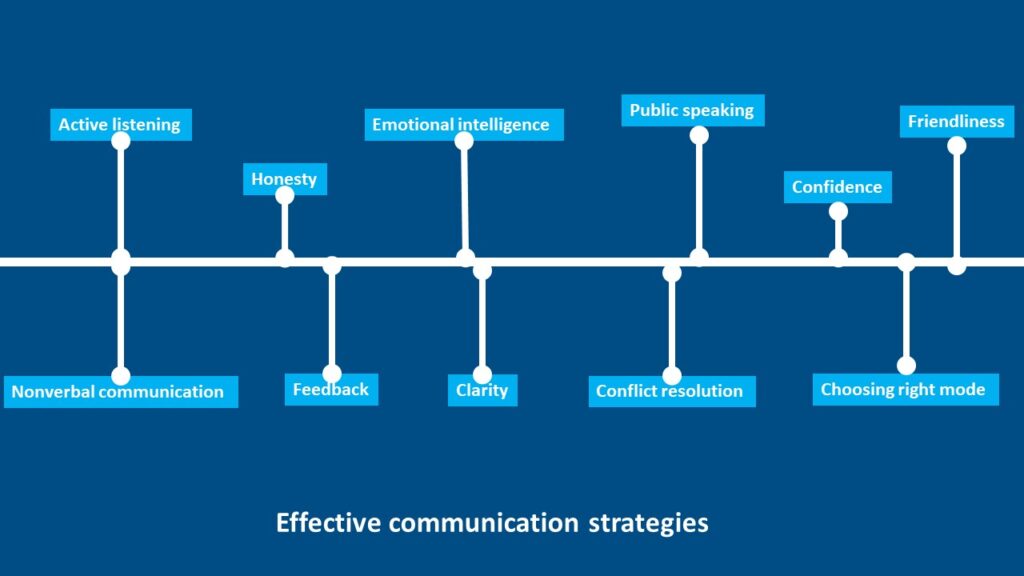
- Active listening
- Nonverbal communication
- Feedback
- Confidence
- Honesty
- Clarity
- Public speaking
- Emotional intelligence
- Conflict resolution
- Friendliness
- Choosing the right mode of communication
Active Listening: Active listening is a strategies of communication skill where the listener listened to the speaker carefully.
Nonverbal communication: Nonverbal communication is a type of communication skill where the information transfer one person to another without use of any word or spoken language.
Feedback: In communication feedback is the response, reaction or information that the receiver of the message gives to the sender.
Confidence: Confidence is a crucial component of effective communication. That can help you get what you want and need and stand up for yourself and your values.
Honesty: Honesty in communication means that in writing, and in speech and other nonverbal communication you are straightforward in expressing the truth without misleading.
Clarity: Ensure your message is clear and easy to understand. Avoid jargon, ambiguity and complexity.
Public Speaking: Public speaking improves overall communication skills. Individuals learn to articulate ideas clearly, engaged audience effectively and become a effective listener.
Emotional intelligence: Emotional intelligence is the ability to both your own emotions and understand the other people’s emotions who are around you.
Conflict resolution: Conflict resolution is the process of ending dispute and reaching an agreement that satisfies all parties involved. conflict resolution.
Friendliness:
Friendly traits like honesty and kindness that can help foster trust and understanding when communicating at work and inside everyone’s family
Choosing the right mode of communication:
Everybody should choose the right mode of communication because it’s the only way to meet people’s individual needs and enable Important human connection
Barriers to communication
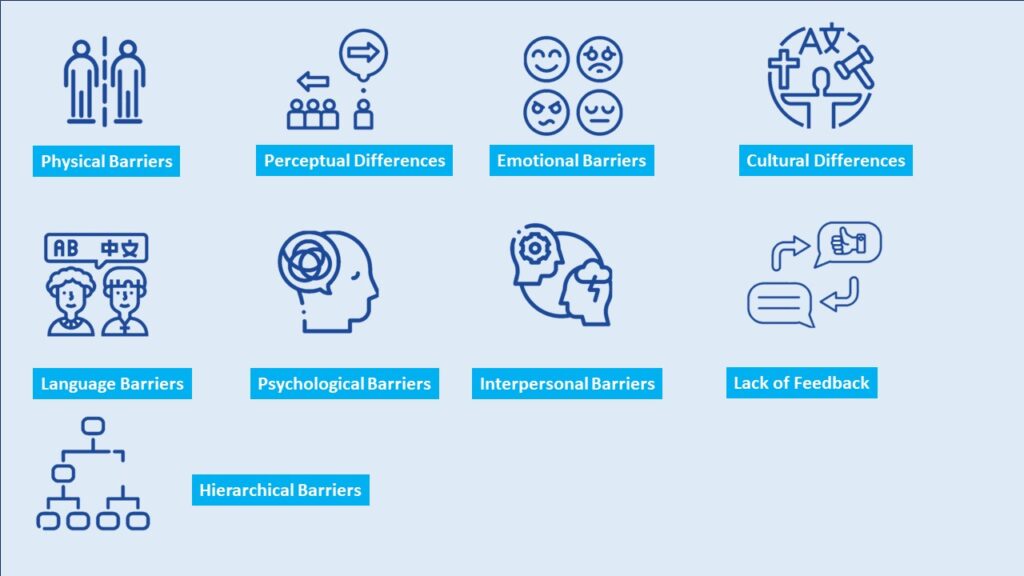
- Physical Barriers
- Perceptual Differences
- Emotional Barriers
- Cultural Differences
- Language Barriers
- Psychological Barriers
- Interpersonal Barriers
- Lack of Feedback
- Hierarchical Barriers
Physical Barriers: These include distance, noise, poor lighting, or any environmental factors that impede effective communication.
Perceptual Differences: Different interpretations of the same message due to varying personal experiences, values, or beliefs can create barriers to effective communication
Emotional Barriers: Strong emotions like anger, fear, or sadness can cloud judgment and impede effective communication by distorting the intended message or blocking receptivity.
Cultural Differences: Diverse cultural backgrounds may result in different communication norms, values, and perceptions. Misinterpretations can occur due to differing cultural contexts.
Language Barriers: When parties involved in communication speak different languages or use technical jargon that isn’t understood universally, it can lead to misunderstandings.
Psychological Barriers: Individual mental states such as stress, anxiety, fear, or preconceived notions can affect how a message is received, processed, and interpreted
Interpersonal Barriers: When individuals are not fully engaged or interested in the communication process, it can lead to a lack of focus, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation of the message.
Lack of Feedback: Without adequate feedback, it is challenging to ensure that the message was correctly understood, potentially leading to misunderstandings or misinterpretations.
Hierarchical Barriers: Power dynamics within organizations or social structures can inhibit open communication, as individuals may feel hesitant to express themselves freely due to fear of repercussions or judgment.

